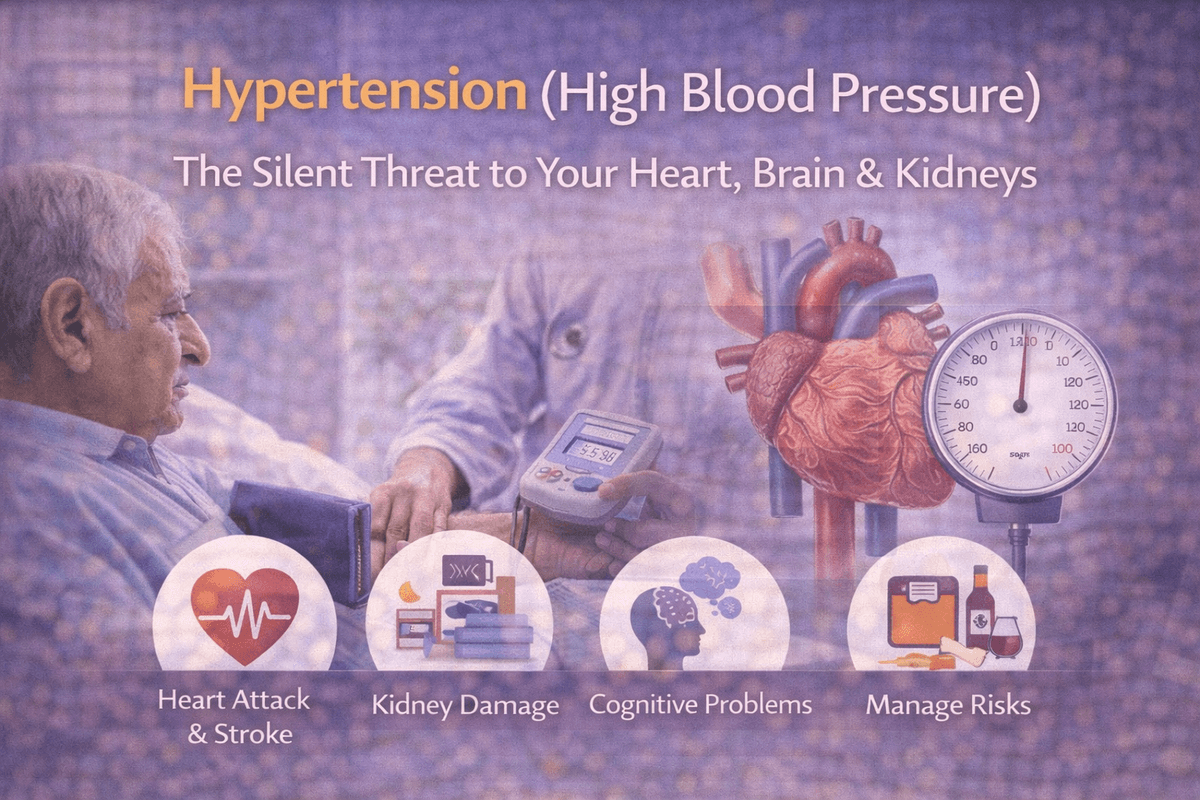
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is one of the most widespread health conditions in the world—and one of the most misunderstood. Often called the “silent killer,” it can quietly damage the body for years without causing obvious symptoms. By the time problems appear, serious harm may already have occurred. Understanding hypertension early is the key to preventing long-term complications and protecting overall health.
Blood pressure is the force with which blood pushes against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps. When this pressure remains consistently high, it is called hypertension. Over time, this excess pressure strains blood vessels and vital organs such as the heart, brain, kidneys, and eyes. Hypertension is usually diagnosed when blood pressure readings are consistently 140/90 mmHg or higher, though doctors may recommend treatment even at lower levels depending on overall risk.
The most concerning aspect of high blood pressure is that most people feel completely normal. There may be no pain, no discomfort, and no warning signs. Yet, silently, high blood pressure increases the risk of: Heart attack and heart failure Stroke and brain damage Kidney disease Vision loss Cognitive decline In older adults, uncontrolled hypertension also increases the risk of falls, dizziness, and medication complications.
Hypertension can affect anyone, but certain factors raise the risk significantly. These include increasing age, family history, lack of physical activity, high salt intake, excess body weight, chronic stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, and conditions such as diabetes or kidney disease. With age, blood vessels naturally lose elasticity, making high blood pressure more common in the elderly.
While many people have no symptoms, some may experience headaches, dizziness, blurred vision, chest discomfort, or shortness of breath—especially when blood pressure is very high. These symptoms should never be ignored and require immediate medical attention.
The good news is that hypertension is highly manageable. Treatment usually involves a combination of lifestyle changes and, when necessary, medication. Healthy eating with reduced salt, regular physical activity like walking, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol can significantly lower blood pressure. For many people, medications are essential and must be taken consistently as prescribed—even when they feel well. Regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial, especially for older adults.
For elderly parents, managing hypertension can be challenging. Forgetting medications, irregular check-ups, or misunderstanding dietary advice are common issues. Family support—through reminders, encouragement, and monitoring—plays a major role in preventing complications.
Hypertension may be silent, but its consequences are not. The condition does not need to control your life—with awareness, regular monitoring, and the right care, blood pressure can be managed effectively. The most powerful step is the simplest one: know your numbers. Early detection and consistent care can protect the heart, brain, and future quality of life—for yourself and for the ones you love.

Copyright ©2025 ripplehealthcare.in
All Rights Reserved